Have you often heard these two organisms grouped together; both mold and bacteria? Although we may hear mold and bacteria similarly grouped together, we know that these two terms contain different hazards and conditions within your indoor environment, and conversely to your health if exposure occurs. Mold is the threatening fungi that can grow unexpectantly and rapidly inside of your home – leaving slight discoloration on the walls, a musty odor throughout the air space, and even certain adverse health effects that occupants can experience after longer durations of exposure. Whereas bacteria is the ominous threat that can become airborne in an environment and slyly make its ways into the human body and trigger a list of potentially weakening effects on a person’s health – whether that be flu-like symptoms and/or symptoms similar to allergies, or even worse more debilitating symptoms depending on the bacteria you are exposed to in your indoor space.
However, even though mold and bacteria may sometimes be lumped together are they the same thing – is mold a bacteria? There are a lot of questions that may surround these two organisms, particularly how they both work, how they form in the environment, there risks to human health, and even the process of protecting your home and your health from exposure to both mold and mildew. Therefore, we are going to learn more about mold and bacteria, their correlation with one another, and how best to mitigate and remove these two organisms from your indoor environment’s air space.
In this article we will discuss more on is mold a bacteria, understand the differences between mold and bacteria, and figure out the best solutions to use in your home to effectively remediate and eliminate both mold and bacteria from the indoor space of your home.

Is Mold Bacteria or a Fungi?
Mold may not be a stranger to many households, as this organism is likely to grow in a multitude of environments including homes and other indoor spaces, as well as outdoor environments. According to Mold Bacteria Facts, there are thousands of known species of molds, which all will act in various ways when present in an environment; with some containing/producing more toxic substances than other species of mold. Although there are various types of mold species that can form in an environment, the conditions that are needed for mold growth will be the same and these conditions include moisture, humidity, darkness, food source, and oxygen.
This versatile and diverse mold species is often misclassified as a bacteria, however, ultimately mold is a fungus that grows in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. There are two types of fungi that are important to understand when it comes to mold growth; filamentous and yeasts. Fungal yeast reproduces by budding and filamentous fungi reproduce by branching or elongation. Whereas, when talking about bacteria, bacteria will regenerate by binary fission which means each parent cell divides into two smaller cells, typically of similar size. Thus, mold and bacteria are both microorganisms, but they are not and do not act in the same manners when it comes to their structure and reproduction.
Mold vs Bacteria
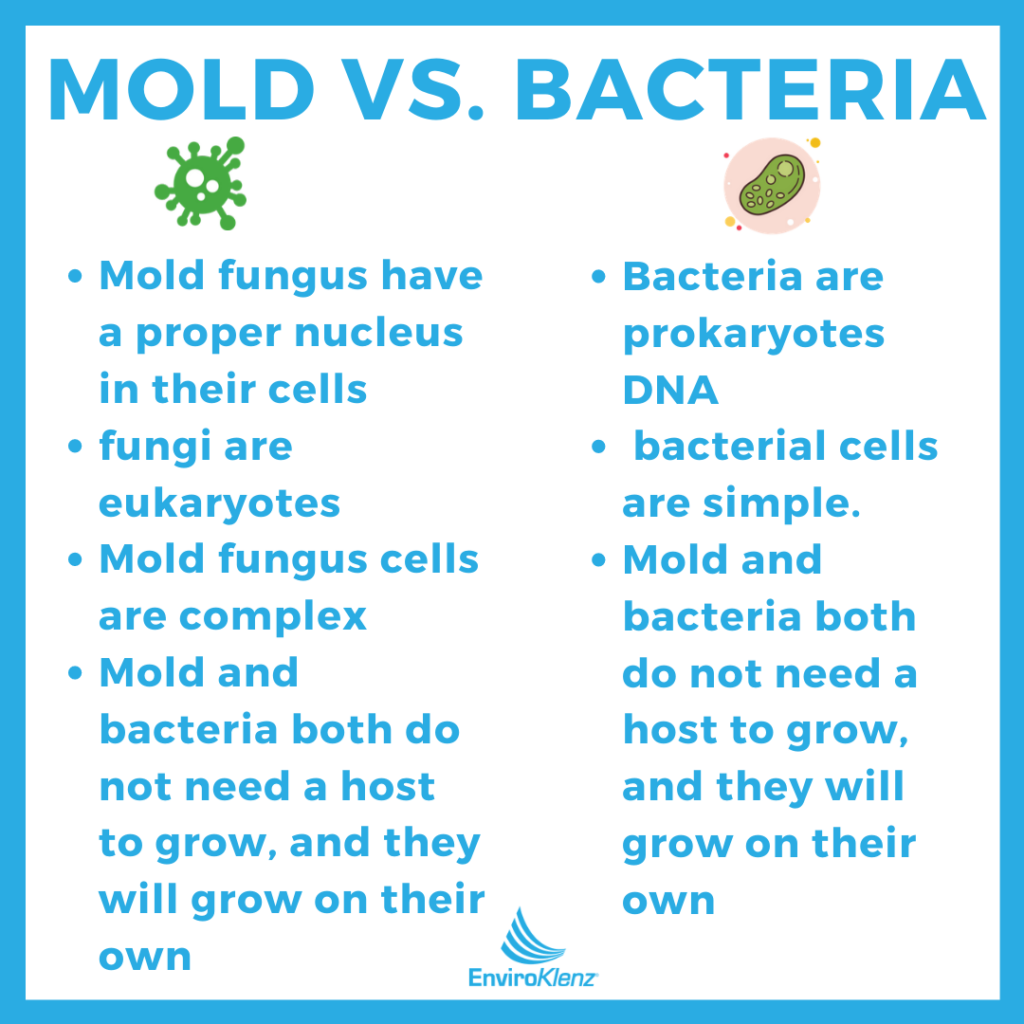
The comparison between mold and bacteria is one that may be confusing to a lot of people, as they are two separate organisms that can be present in an indoor environment that will act differently and effect the environment and health of those in this space. As we discussed previously, there are several key differences between both mold and bacteria – such as the structure of both of these organisms and how they both reproduce in the environment. In addition to these main differences, there also other characteristics that helps you distinguish between both mold and bacteria such as;
- Mold fungus will have a proper nucleus in their cells and bacteria will not.
- Bacteria are prokaryotes that’s DNA is not separated from the cytoplasm in a nucleus, whereas fungi are eukaryotes that’s DNA is enclosed in a nucleus which is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane.
- Mold fungus cells are complex while bacterial cells are simple.
- Mold and bacteria both do not need a host to grow, and they will grow on their own.
What Causes Mold to Grow
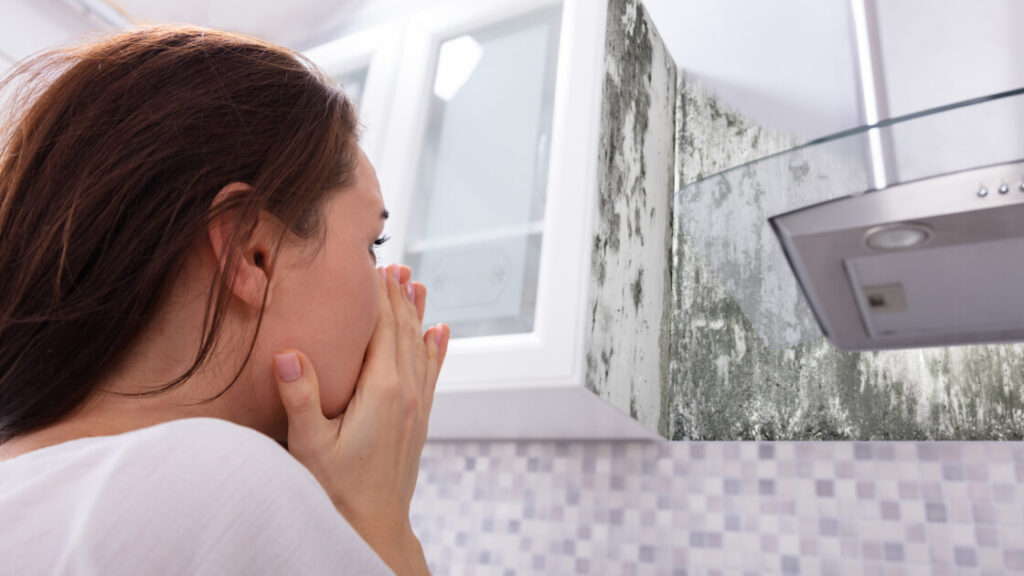
If you have found that mold is growing inside of your home, you may be shocked to discover this growth within your indoor space and wonder what exactly caused this mold to begin its development on the surfaces. According to Moldpedia, mold will need certain conditions within an indoor space to provide the optimal environment for mold development – these conditions will include mold spores, a food source (wood, drywall, cotton), darkness, warmth, oxygen, moisture, and time for mold to grow. All of these conditions will allow for the perfect environment for mold to grow, but in reality, you really only need moisture present for mold to develop and thrive in an indoor space.
In addition to moisture, another important condition that allows for mold growth is humidity. If you live where humidity in the air is naturally high, your home may become more susceptible to mold growth that may become a problem for both your indoor air quality and the health of those occupants in this space that are frequently exposed to the mold. Humidity can also easily form from moisture that is already present inside of your home, that will evaporate into the air and increase the humidity levels in the space.
Does Mold Make You Sick?
Can mold make you sick? Mold is a term that can send homeowners into a state of panic, due to its inherent toxicity and hazards that it can produce into the environment – especially when certain species of mold produce mycotoxins or other toxic substances into the air. However, the dangerous components of mold that can be emitted into the air that comes from all mold species are reproductive mold spores. Mold spores are tiny reproductive cells that are easily released into the air, and an enclosed space will amplify their ability to make contact with an individual in the space. These small mold spores can reach into the deepest recesses of the lungs and will ultimately stir a range of symptoms within a person’s body.
Many people will form what is known as a mold allergy, which will occur when your immune system overreacts when you breathe in mold spores that are produced within your indoor environment from already existing mold growth(s). This type of allergy can trigger a variety of symptoms such as coughing, eye irritation, and other allergy-related symptoms, according to Mayo Clinic. In some individuals, this allergy to mold can also be linked to asthma and when mold exposure happens to these asthmatic individuals it can lead to restricted breathing and other airway symptoms. Overall, though when it comes to the impact that mold will have especially when discussing if mold will make you sick, this will depend on each individual, their exposure amounts, and their preexisting health problems such as allergies, asthma, and other respiratory problems.
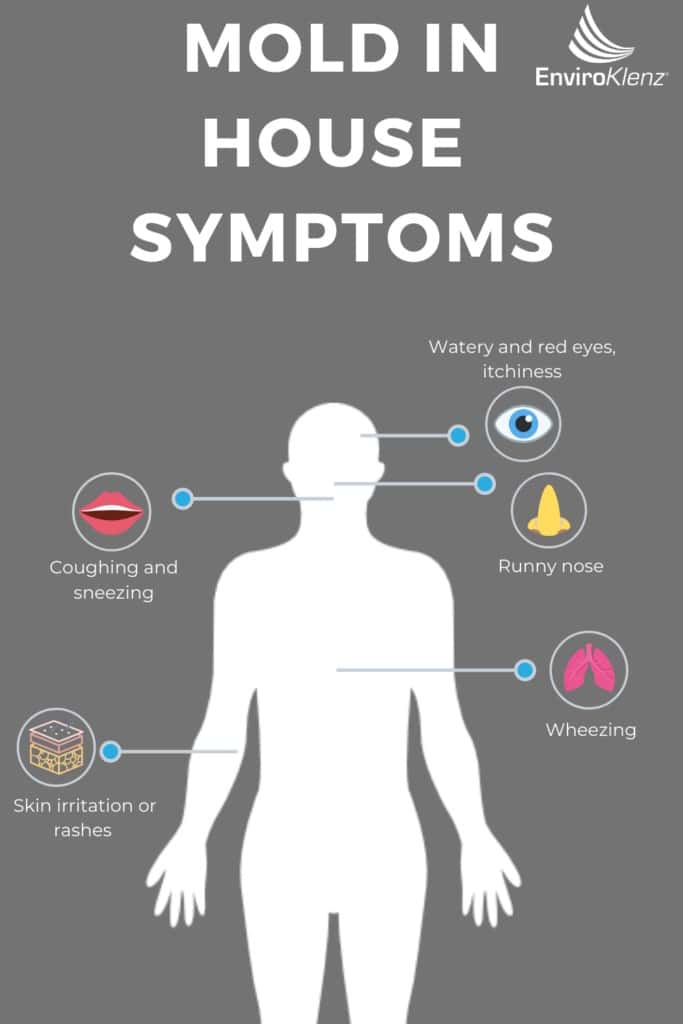
Mold in House Symptoms
As we discussed previously, mold fungus is known for producing various irritating substances into the environment that can act as allergens in the air space that will trigger adverse health effects in many individuals. Often times, when mold is growing inside of your home, many homeowners may not even be aware that mold is present in their indoor personal air space. Identifying mold in a home can be difficult, and sometimes the first signs of mold growth in a home can be health symptoms that are triggered whenever the individual is present in the environment. Mold can potentially cause allergy-like symptoms in some individuals and in others there may even be no reaction to mold unless they are exposed to the mold’s reproductive spores in their indoor air.
When it comes to reactions that a person will have when exposed to mold, an allergic reaction to the mold is the most common and therefore the greatest potential health risk of mold. According to the Medicine Net, symptoms and signs of mold allergy may include the following symptoms;
Do HEPA Filters Remove Bacteria and Mold in Air?
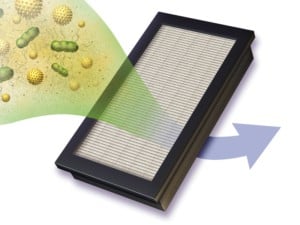
When it comes to air filtration that can be utilized in indoor environments to remove and mitigate certain airborne pollutants from a home or other personal indoor space, the capturing and removal of small particulates in the air such as mold spores and bacteria can be difficult to accomplish. There are a variety of various air filtration technologies that are used in air purifiers today that will work specific to remove certain contaminants from the air, and these technologies can include ozone, ionization, carbon, and HEPA filtration. HEPA filters (High Efficiency Particulate Air Filter) is an extremely effective air filter that works specifically to filter out particulate matter such as dust, dander, mold spores, bacteria, viruses, etc.
HEPA filters are bestowed this name based on their ability to capture fine particulate matter larger than 0.3 microns on its media surface – and this can include all particles that can reach into your lungs, with 0.3 microns in size being the smallest size particle to enter into the human lungs. As the airborne contaminants collide with the HEPA’s fibers and become trapped, it will keep effectively filtering out both small and large contaminants from the air. The dense media filter of the HEPA filter allows for it to trap those fine particulate matter like microorganisms (mold spores, viruses, and bacteria) and be able to collect them and trap them in the filter while still working for up to 2 years – depending on the type of HEPA filter that is used in the air purifier.
Hospital-Grade HEPA Filter for Mold Removal
One of the best ways to kill mold spores in the air naturally is through the use of air purification devices or air filtration solutions. Air purifiers are devices that work through specific filtration methods to clean the indoor air and remove pollutants that may be traveling in the air space. Each air purifier contains a different type of filtration method that will all work in specific ways and to filter certain types of pollutants in the air – such as chemicals, odors, allergens, or even pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and airborne mold spores.
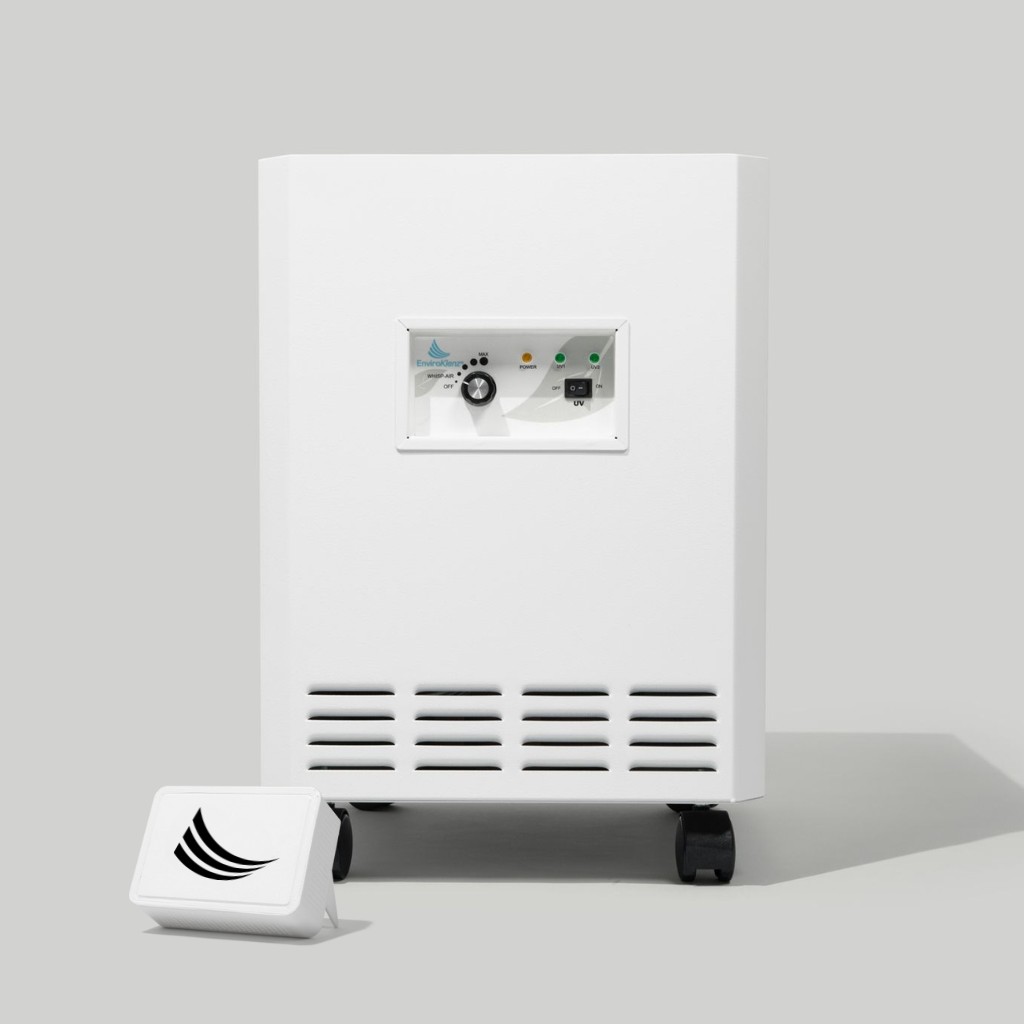
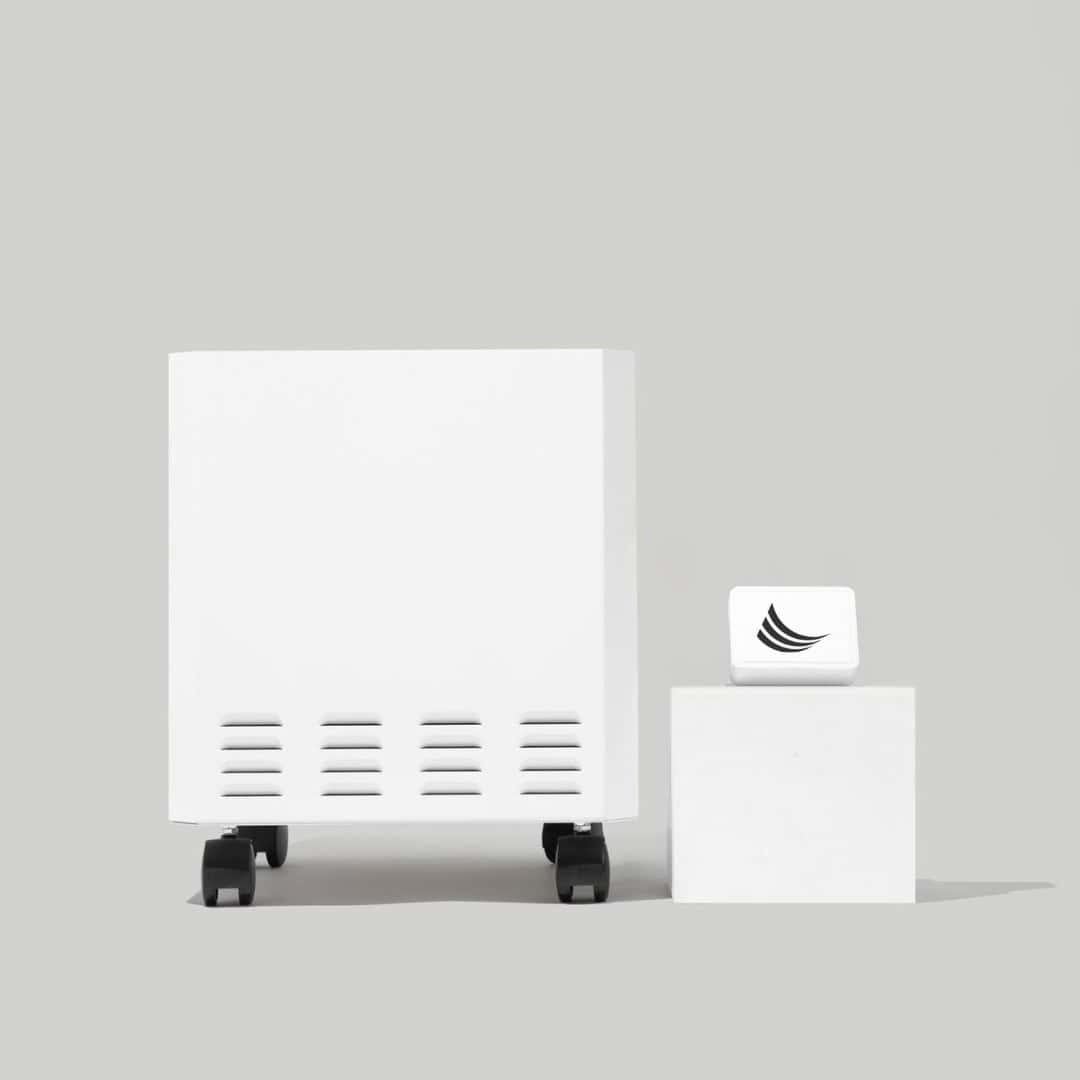
The EnviroKlenz UV Air Purifier is an effective air purification device that is capable of inhibiting the growth of captured microorganisms (such as bacteria, mold, and viruses). This UV Air Purifier combines the Advanced EnviroKlenz technology for toxic and noxious chemical and odor removal with HEPA filtration and ultraviolet germicidal radiation (UVC) to remove airborne particulates and allergens, as well as microorganism destruction. The HEPA filter’s ability to capture these fine particulate matters from the air and trap them within the dense media filter of this HEPA material allows for the EnviroKlenz UV Air Purifier to do its job of collecting and destroying both mold spores and bacteria from the air. Therefore, having an air purifier like the EnviroKlenz UV Air System in your home can help to capture and remove those airborne mold spores from the air to minimize health risks to the occupants of the home.

Article Sources:








